Our brains are made up of complex neural networks. Within these networks, “neurotransmitters” play the role of transmitting information. Neurotransmitters play a crucial role in supporting our mental and physical activities, including emotions, thoughts, and behaviors. In this article, we will delve into the types of major neurotransmitters, their detailed functions, and how they impact our daily lives, with specific examples.
Neurotransmitter Transmission Mechanism: The Mystery of Synaptic Transmission
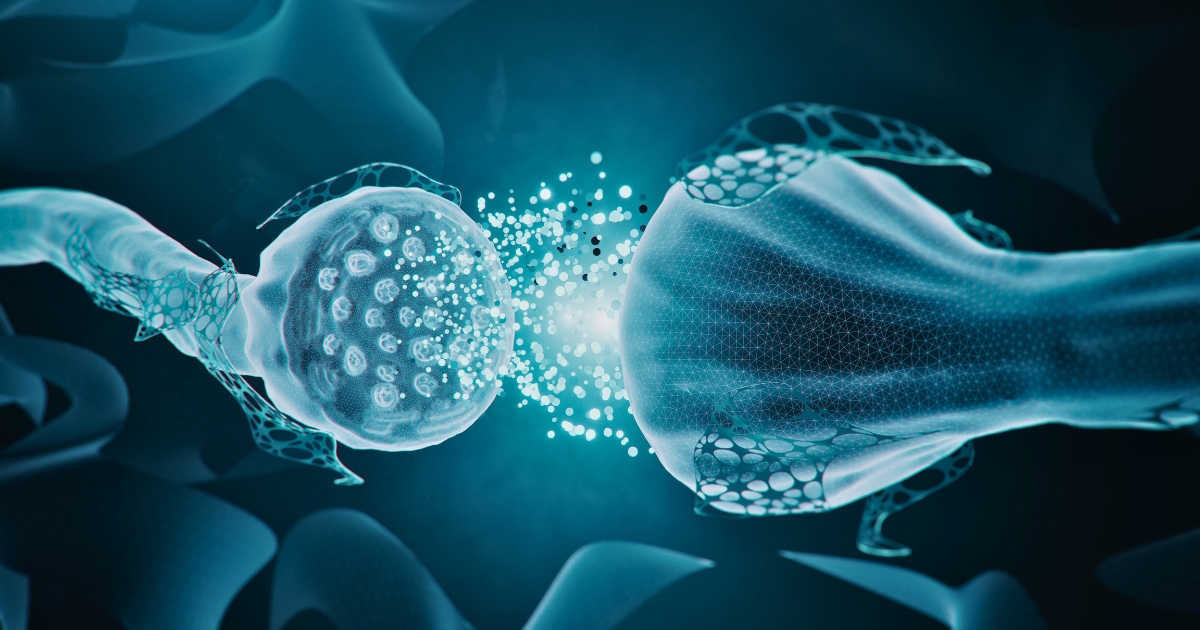
Neurotransmitters are stored in small sacs called synaptic vesicles at the ends of nerve cells (neurons). When a neuron is excited, a change in electrical potential occurs, causing the neurotransmitter to be released from these synaptic vesicles. Neurotransmitters drift across a tiny space called the synaptic cleft and bind to specific proteins called receptors on the cell membrane of the next neuron. By binding to receptors, neurotransmitters transmit information to the next neuron, triggering either excitatory or inhibitory responses. This entire process is called synaptic transmission, and it is through this constant synaptic transmission in our brains that information is transmitted and processed.
Synaptic transmission occurs with remarkable speed and accuracy. It is estimated that thousands of synaptic transmissions occur per second, and it is this astonishing speed and accuracy that allows us to perform complex thoughts and actions instantaneously.
Major Neurotransmitters and Their Roles: The Source of Emotions, Thoughts, and Actions
Serotonin
Regulates mood, sleep, appetite, and plays a role in maintaining mental balance. When serotonin secretion is appropriate, it is said that the mind is stable, and feelings of happiness and relaxation are obtained. For example, if serotonin is deficient, it can lead to a depressed mood and poor sleep quality.
Dopamine
Involved in various aspects such as motivation, pleasure, motor function, learning, memory, and attention. Dopamine is secreted during moments when we feel joy and pleasure, such as achieving goals or making new discoveries. Dopamine has the effect of increasing our motivation to achieve something and promoting our desire to learn.
Acetylcholine
Plays a role in memory, learning, attention, arousal, and muscle contraction. It plays an important role in acquiring new knowledge and recalling past experiences. Acetylcholine also facilitates the transmission of information between motor nerves and muscles, aiding in muscle contraction.
GABA (Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid)
Suppresses excitation in the brain, providing relaxation and sedation effects. It is secreted when we feel stress or anxiety and works to calm the mind and body. GABA also has a sleep-promoting effect, contributing to high-quality sleep.
Glutamate
Plays a central role in learning and memory and is deeply involved in neuroplasticity (the brain’s ability to change neural circuits). Glutamate is secreted abundantly when the brain is actively working. Glutamate has the function of strengthening neural circuits in the brain, enabling efficient learning and memory.
Other Neurotransmitters and Their Roles
- Norepinephrine: Plays a role in stress response, arousal, concentration, and attention enhancement. It also has the effect of increasing heart rate and blood pressure.
- Histamine: Secreted upon waking up or during activity, it works to maintain wakefulness. It is also involved in allergic reactions and inflammatory responses.
- Endorphins: Neurotransmitters that suppress pain and bring about feelings of happiness and euphoria. They are said to be secreted during exercise or laughter.
- Oxytocin: Known as the “love hormone,” it enhances feelings of love and trust, playing an important role in building and maintaining relationships. It is also secreted during childbirth and breastfeeding, deepening the bond between mother and child.
- Orexin: Maintains wakefulness and promotes appetite. A deficiency in orexin can lead to sleep disorders such as narcolepsy.
Conclusion: Towards a Better Life Through Understanding Neurotransmitters
Neurotransmitters play a crucial role in controlling our emotions, thoughts, and behaviors. By understanding the functions of these substances, we can gain a deeper understanding of our own mental and physical health. To maintain a balance of neurotransmitters, it is important to have regular lifestyle habits, a balanced diet, moderate exercise, and stress management.
Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. If you are experiencing any mental or physical discomfort, please consult a medical professional.